Traumatic Extra-cranial Bleeding
Each year, worldwide nearly six million people die from trauma – many after reaching the hospital
Among trauma patients who survive to reach the hospital, extra-cranial bleeding is a common cause of death, accounting for around 40% of in-hospital deaths
Research Overview
The CRASH-2 trial of TXA for traumatic haemorrhage
The CRASH-2 trial evaluated the effect of TXA on death and vascular occlusive events in patients with traumatic bleeding.
A total of 20,211 adult trauma patients with significant bleeding, who were within 8 hours of their injury, were randomly allocated to receive TXA (1 g over 10 min followed by an infusion of 1 g over 8 h) or matching placebo.
The CRASH-2 trial results showed TXA significantly reduced all-cause mortality in bleeding trauma patients but should be given as early as possible. Treatment within three hours of injury reduces death due to bleeding by about one-third (Relative Risk (RR) = 0.72 (0.63 – 0.83); p<0.001 ).
There was strong evidence that the effect of TXA on death due to bleeding varied according to the time from injury to treatment.
Early treatment (≤1 h from injury) significantly reduced the risk of death due to bleeding (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.57-0.82; p<0.0001). Treatment given between 1 and 3 hours also reduced the risk of death due to bleeding (RR 0.79, 0.64-0.97; p=0.03).
Treatment given after 3 h seemed to increase the risk of death due to bleeding (RR 1.44, 1.12-1.84; p=0.004). No increase in vascular occlusive events was observed.
On the basis of these results, tranexamic acid was added to the WHO’s Essential Medicines List and to trauma protocols worldwide.
More Resources
Click on watch, read or teach to access videos, publications, and training materials
![]() CRASH-2 Trial Results
CRASH-2 Trial Results
An analysis of the 2010 CRASH-2 study shows that TXA should be given as early as possible to bleeding trauma patients; if treatment is not given until three hours or later after injury, it is less effective and could even be harmful.
![]() CRASH-2: TXA Tranman Video
CRASH-2: TXA Tranman Video
The award-winning TRANMAN video uses unusual visuals to tell the results of the CRASH-2 trial
![]() CRASH-2: TXA Saves Lives
CRASH-2: TXA Saves Lives
![]() CATALYST: Episode on Bleeding Trauma
CATALYST: Episode on Bleeding Trauma
Episode from Australian TV show, Catalyst focusing on traumatic injuries, what these injuries can do to the blood, and the important role of TXA in treatment of these injuries
![]() TXA in CASUALTY
TXA in CASUALTY
A scene from the TV show Casualty where a patient with a femoral arterial stab wound is treated with TXA
![]() Karim Brohi discusses Tranexamic Acid in Trauma
Karim Brohi discusses Tranexamic Acid in Trauma
![]() CRASH-2 Trial – Comments from Collaborators – Spanish Version
CRASH-2 Trial – Comments from Collaborators – Spanish Version
![]() CRASH-2 Trial Results
CRASH-2 Trial Results
Effects Of Tranexamic Acid On Death, Vascular Occlusive Events, And Blood Transfusion In Trauma Patients With Significant Haemorrhage (Crash-2): A Randomised, Placebo-controlled Trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: TXA Manga Style
CRASH-2 Trial: TXA Manga Style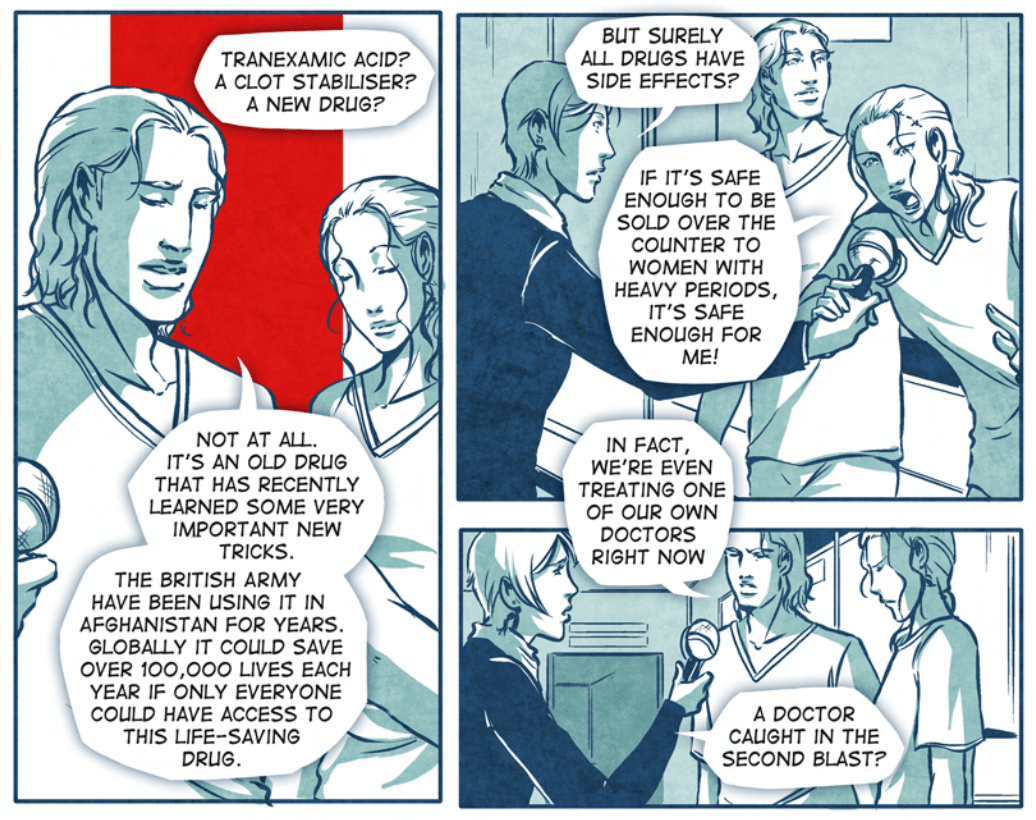
Clinicians are bombarded with thousands of pieces of new information every day. CRASH-2 used a unique Manga-style approach to help communicate the results of the CRASH-2 trial. See the drama ensue when doctors and nurses work to save patients bleeding from traumatic injuries
Read the story
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Time
CRASH-2 Trial: Time
The Importance Of Early Treatment With Tranexamic Acid In Bleeding Trauma Patients: An Exploratory Analysis Of The Crash-2 Randomised Controlled Trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Baseline Risk
CRASH-2 Trial: Baseline Risk
Effect of tranexamic acid on mortality in patients with traumatic bleeding: prespecified analysis of data from randomised controlled trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Intracranial Bleeding
CRASH-2 Trial: Intracranial Bleeding
Effect of tranexamic acid in traumatic brain injury: a nested randomised, placebo controlled trial (CRASH-2 Intracranial Bleeding Study)
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Economics
CRASH-2 Trial: Economics
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Administering Tranexamic Acid to Bleeding Trauma Patients Using Evidence from the CRASH-2 Trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Deaths Averted
CRASH-2 Trial: Deaths Averted
Avoidable mortality from giving tranexamic acid to bleeding trauma patients: an estimation based on WHO mortality data, a systematic literature review and data from the CRASH-2 trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Interaction Not Confounded
CRASH-2 Trial: Interaction Not Confounded
Tranexamic acid in bleeding trauma patients: an exploration of benefits and harms
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Exploring Mechanisms
CRASH-2 Trial: Exploring Mechanisms
Mechanism of action of tranexamic acid in bleeding trauma patients: an exploratory analysis of data from the CRASH-2 trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Generalisability
CRASH-2 Trial: Generalisability
Applying results from clinical trials: tranexamic acid in trauma patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Trauma Promise
CRASH-2 Trial: Trauma Promise
A promise to save 100 000 trauma patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Policy Promise
CRASH-2 Trial: Policy Promise
Tranexamic acid in trauma: we need stronger global health policy
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Heart Technology Assessment Report
CRASH-2 Trial: Heart Technology Assessment Report
The CRASH-2 trial: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of the effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and transfusion requirement in bleeding trauma patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Effect of Treatment Delay on the Effectiveness and Safety of Antifibrinolytics in Acute Severe Haemorrhage
CRASH-2 Trial: Effect of Treatment Delay on the Effectiveness and Safety of Antifibrinolytics in Acute Severe Haemorrhage
A Meta-analysis Of Individual Patient-level Data From 40138 Bleeding Patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial Meta-Analysis: Effect of Delayed TXA treatment
CRASH-2 Trial Meta-Analysis: Effect of Delayed TXA treatment
Effect of treatment delay on the effectiveness and safety of antifibrinolytics in acute severe haemorrhage: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data from 40138 bleeding patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Antifibrinolytic Therapy
CRASH-2 Trial: Antifibrinolytic Therapy
New data and new concepts
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Consent Rituals on Mortality
CRASH-2 Trial: Consent Rituals on Mortality
Effect of consent rituals on mortality in emergency care research
View PDF
![]() The CRASH-1 Trial Collaborators
The CRASH-1 Trial Collaborators
Final results of MRC CRASH, a randomised placebo-controlled trial of intravenous corticosteroid in adults with head injury-outcomes at 6 months
View PDF
![]() The CRASH-1 Trial Collaborators
The CRASH-1 Trial Collaborators
Effect of intravenous corticosteroids on death within 14 days in 10,008 adults with clinically significant head injury (MRC CRASH Trial): a randomised placebo-controlled trial
View PDF
![]() Analysis of the CRASH-2 and WOMAN trials
Analysis of the CRASH-2 and WOMAN trials
Risk factors for blood transfusion in traumatic and postpartum hemorrhage patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Implementation of tranexamic acid for bleeding trauma patients
CRASH-2 Trial: Implementation of tranexamic acid for bleeding trauma patients
A longitudinal and cross-sectional study
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Is tranexamic acid effective in traumatic brain injury?
CRASH-2 Trial: Is tranexamic acid effective in traumatic brain injury?
Evidence for an effective therapy
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: TXA In Trauma Patients
CRASH-2 Trial: TXA In Trauma Patients
Applying results from clinical trials
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Prognostic Model
CRASH-2 Trial: Prognostic Model
Predicting early death in patients with traumatic bleeding: development and validation of the prognostic model
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Correspondence
CRASH-2 Trial: Correspondence
The CRASH-2 trial was not about global scientific supremacy
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: An Analysis of CRASH-2 Cohort
CRASH-2 Trial: An Analysis of CRASH-2 Cohort
Risk Factors for Vascular Occlusive Events and Death Due to Bleeding in Trauma Patients
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Antifibrinolytic drugs for acute traumatic injury
CRASH-2 Trial: Antifibrinolytic drugs for acute traumatic injury
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: An Example in TBI
CRASH-2 Trial: An Example in TBI
Covariate adjustment increased power in randomized controlled trials
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Clinical Randomisation of an Antifibrinolytic in Significant Haemorrhage intracranial bleeding study
CRASH-2 Trial: Clinical Randomisation of an Antifibrinolytic in Significant Haemorrhage intracranial bleeding study
The effect of tranexamic acid in traumatic brain injury–a nested randomised, placebo-controlled trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Rationale & Overview
CRASH-2 Trial: Rationale & Overview
Tranexamic acid for the treatment of significant traumatic brain injury: an international randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Protocol Summary
CRASH-2 Trial: Protocol Summary
A large randomised placebo controlled trial among trauma patients with or at risk of significant haemorrhage, of the effects of antifibrinolytic treatment on death and transfusion requirement
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Statistical Analysis Plan
CRASH-2 Trial: Statistical Analysis Plan
View PDF
![]() CRASH-2 Trial: Presentation
CRASH-2 Trial: Presentation
Tranexamic acid safely reduces mortality in bleeding trauma patients. Here we present the evidence
View PDF
More Treatments
TXAcentral is a resource for health professionals caring for people with acute bleeding
TXAcentral brings together randomised trial evidence on the effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid
Data on many of the trials are also available at the freeBIRD website
In trauma patients with significant bleeding and those with traumatic brain injury (TBI), TXA has been shown to reduce mortality in both extracranial and intracranial bleeding
Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal death worldwide, responsible for around 100 000 deaths each year. TXA given as quickly as possible after birth and no later than 3 hours, reduces death due to bleeding and the need for surgery to stop bleeding
GI Bleeding is a common emergency that causes substantial mortality and morbidity worldwide. TXA was found to not reduce deaths from GI bleeding and showed an increased risk of thromboembolic events
Every year there are over 300 million surgical procedures worldwide. Bleeding is an important complication and many patients require a blood transfusion. TXA reduces blood loss in surgical patients by about one‐third. However, the effects of TXA on thromboembolic events and mortality in surgery are uncertain
There is ongoing research looking at how Tranexamic Acid (TXA) could be utilised for other bleeding conditions